Module for
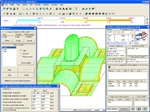
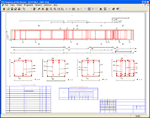
analysis and design of reinforced concrete structures LIR-ARM is used to determine areas of reinforcement for columns, beams, slabs and shells according to ultimate limit states and serviceability limit states. LIR-ARM module supports building codes of different countries. Design model and forces are imported from LIR-VISOR module. It is possible to assign arbitrary properties of concrete and reinforcement that is useful for analyses of reconstruction. In this module you can unite several elements of the same type into one structural element (STE) and arrange reinforcement along the whole length of this element. Drawing of beams and columns are presented after analysis and can be saved as DXF files.
The following building codes are supported:
− SNIP 2.03.01-84;
− TSN-100;
− DSTU 3760-98;
− SNIP 52-01-2003;
− Eurocode 2 (according to ultimate limit states only).
Reinforcement in plate elements (wall-beams, slabs, shells) is analysed according to Wood theory for Eurocode 2 and according to N.I. Karpenko method for other building codes.
To determine reinforcement in bar elements, we realize general iteration optimizing methods that allow you to analyse sections of arbitrary shape (rectangular, cross, T-sections, I-sections, box, angle, circle, ring sections) using similar methods. The sections may have arbitrary location of reinforcement determined for different types of stress state (simple bending, oblique bending, bending with torsion, plane eccentric compression-tension, simultaneous action of all six types of forces – Mx, My, N, Qx, Qy, Mx).
In iteration algorithms, the following optimization principles are included: reinforcement is increased mainly in the most stressed parts of the section, mutual influence of reinforcement determined by DCF or DCL is also taken into account. These algorithms meet the requirements for flexibility, because the user will be able to assign the mode for analysis of reinforcement:
− to select type of reinforcement pattern in the section (symmetrical relative to one or two principal axes of the section, uniform location of reinforcement along the specified edges, arbitrary location of reinforcement);
− to assign mode ‘corner rebars’ where the general algorithm increases area of reinforcement primarily in corner parts. In some cases this approach allows you to reduce amount of reinforcement by 20-30% in comparison with other types of reinforcement pattern in the section;
− to assign limit diameters of reinforcement bars (rebars) for analysis of reinforcement according to serviceability limit state because smaller diameters improve resistance of RC element to crack formation and in this case area of necessary reinforcement could be noticeably less;
− to manage parameters of iteration process, reduce the analysis precision a little (in this case accuracy may be 3-5%) but significantly increase operating speed of algorithm and vice versa.
LIR-ARM module contains extensive Help system where you can find detailed information about options and tools of the module.

 LIRA
LIRA